What is “Search, Plus Your World” and Why Is It Important?
1 FebWhat is “Search, Plus Your World”?
Last month Google released its latest changes to their search algorithm called “Search, Plus Your World”. Essentially the changes mean that now the search results presented on Google will be even more tailored to each and every individual.
The important thing to remember is Google’s business model and their mission, which is to provide the searcher with the most qualified results.
Why do they want to do that? Well it’s quite simple – if they provide the search user with search results that do not meet the user’s expectations, then the user will move to another search engine such as Yahoo or Bing. If the searcher then finds those results are better suited, then next time they are looking for an answer they will bypass Google and go elsewhere.
Now of course Google don’t want this. Google wants you to use its plethora of services: Google docs, YouTube, Gmail etc, because if users switch to another search engine then they will start to lose advertising revenue. This is important because advertising revenue is Google’s largest income stream.
So what Do the Latest Changes Mean?
If you combine this change with the Panda update of last year and Google’s social media strategy Google+, then I think the underlying theme is that you have to create unique quality content that adds real value to your community on a regular basis.
Why Have The Changes Been Made?
Google are aiming to provide each individual user with a unique search experience. Yes, I did say that, a unique search experience. They will do that by taking the organic search results that are gathered by the Google search algorithm and combining that with results shared, reviewed and liked by people in your online community – it could be friends, family or work associates however you categories them.
So for example you want to book a holiday, you go to Google and type in “cheap holiday to Mexico.” In the search results come all the usual airlines, holiday and travel companies but also there is a review from one of your friends.
The review says that they just came back from Mexico they had a great time, the resort was superb and it was really great value.
Now when you see that review, because you already know and perhaps trust that person who has made that review, you will be more inclined to be influenced by their experience than other reviews from other holiday companies.
The same theory applies for any content on the internet. If you write an article or a blog post on small business marketing tips that gets shared by “Bob” on Google+, and somebody in Bob’s following then does a search for small business marketing tips, then your post is likely to appear in the search results because their friend Bob has already recommended it. To make it really personal, there may even be a picture of Bob or a little logo by the side in the search results. It is all about Social proof (Watch the official Google video below).
As you can see it is a pretty important and significant update.
As a small business owner what should you do?
The previous strategy was to get a website or blog, optimize content for relevant search criteria, get some back links and then convert the traffic on the back end. This process will not change, however just churning out content and syndicating it to social media sites will no longer be good enough. You need to make sure that you practice the following:
1. Create top quality content
2. Deliver incredible value with your content.
3. Motivate people to engage with your content. (Like, share, comment)
4. Position yourself as an authority in your niche
5. Listen to your customers and other people in your niche.
6. Comment and share on what is meaningful to you with your community.
Providing incredible value, listening to your community and being meaningful to others will help build your brand and position you as an expert in your field. One thing that is certain is that in an age where the mass of messages multiplies daily, only a small number really matter. Google know this, and that is why they have made the changes. (“Search, Plus Your World” )
If you want your business and brand to have sustainable profit and your messages to influence others, then you need to make sure your message is the one that matters.
Recent Facebook News : Facebook Timeline Now Pushed To Everyone, Users Get A Week To Clean Up Profiles
25 JanYou can run, but you can’t hide. Facebook’s biggest user interface overhaul since the Wall, the Facebook Timeline, is now becoming mandatory for all users. According to the company, over the next few weeks, everyone will get the new Timeline. And here’s the important part: when you do, you’ll have just seven days to preview what’s there now, and hide anything you don’t want others to see.
In case you’re unfamiliar, the Facebook Timeline makes it far easier for you to travel back through your Facebook posts – posts which normally disappeared off your Wall and into oblivion. The posts from these previous months and years are now accessible through new navigational elements on the right-side of your screen that let you quickly travel back in time to the day you were born.
You can fill in data from your pre-Facebook years using the new status update box, which now includes support for adding a specific year and various “life events.” These events include things like marriages, births, deaths, new jobs, trips and vacations, new homes, and other things you might want to record in the scrapbook-like Timeline.
With Timeline’s added ability to find older posts, including those from the days before your boss, grandparents, mom and dad were on Facebook, users will need to do a rapid cleanup on their profiles when the Timeline goes live.
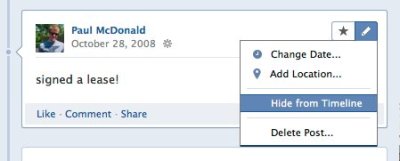
Facebook explains how to hide posts you don’t want to appear on your Timeline (click the pencil to hide, delete or edit a post). You can also use the privacy drop-down to change who can see posts (e.g. “Only Me”).
Previously, users had to go out and get Timeline for themselves. Facebook was specifically trying to not push it too hard. It wouldn’t show News Feed stories announcing your friends had migrated, for example, as the company wanted the Timeline to be an opt-in decision that allowed people enough time to moderate their profile posts. Giving users seven days to do the same is somewhat an extension of that thinking, although could prove troublesome for irregular Facebook users who don’t realize they’ve been migrated, leaving themselves exposed when the week is up.
If you want to be proactive and get the Timeline now, go to the Introducing Timeline page and click “Get Timeline.” Or you can wait until you see an announcement at the top of your profile.
Timeline will also be available on Android, m.facebook.com and iOS.
Original Source : Facebook Timeline Now Pushed To Everyone, Users Get A Week To Clean Up Profiles
Important Google News: Recap for Last Week
24 Jan If you were sick last week or on vacation or in a coma you missed a LOT of Google news. Here is a must read recap of articles on Google, Google changes and Google news.
If you were sick last week or on vacation or in a coma you missed a LOT of Google news. Here is a must read recap of articles on Google, Google changes and Google news.
Industry Related
– Google PR Nightmare: Search Giant Apologizes for Evildoing – SEJ
Google+
– “Ask On Google+” Links Appearing In Google’s Search Results – SEL
– New Gmail, YouTube, Blogger Users Join Google+ by Default – SEW
– New Google account users forced to join Google+ – MSNBC
– Larry Page: Google+ Now Has 90 Million Users – Mashable
– Search Plus Your World: Google and Twitter Exchange Blows – SEJ
– Why Google’s Biggest Problem with ‘Search Plus Your World’ Isn’t Antitrust – Time
– FTC Investigating Google: Google Launches Ad Campaign to Control Damage – SEJ
– Why Google owes you nothing – CNet
Above the Fold
– Pages With Too Many Ads “Above The Fold” Now Penalized By Google’s “Page Layout” Algorithm
– Google Announces Above-the-Fold Algorithm Change – SEJ
– An Interview With A Google Search Quality Rater – SEL
– Does Google Have An Interest In Pinterest? – TechCrunch
– AdWords Search and Display Networks Will Soon Get Impression Share Metrics – SEW
– Is Google Selling Investors Private Search Data? – SEOBook
Non-Industry Related
– Google’s 4Q disappoints as advertising prices sink – AP
– Google Trims The Fat – TechCrunch
– Google’s Mobile Ad Revenues Could Surge To $5.8 Billion In 2012 – TechCrunch
– Google Tops Fortune’s List of Best Places to Work – PCMag
– Google Plays Both Sides in the Web Piracy Fight: Susan Crawford – Bloomberg
– The White House Joins Google+ -White House
– Google Fires Rogue Contractors for Vandalizing Competitor’s Database – SEJ
Introduction To SEO
23 JanSEO (Search Engine Optimization) : SEO stands for “search engine optimization.” The term may sound like optimizing an actual search engine such as Google, however this professional service focuses on tweaking a website to do well – to appear among the top listings on search engine results pages (SERPs). SERPs are web pages returned by search engines like Google or Yahoo! after a user performs a search. These pages contain links to web sites and documents that the search engine deems relevant to the word or phrase. These words or phrases are also known as “keywords.”
 Using complex and proprietary algorithms, search engines consider hundreds of factors when gauging the relevance of a certain site or webpage. Search engines are constantly changing their proprietary algorithms – sometimes significantly – in an attempt to list only the most relevant results.
Using complex and proprietary algorithms, search engines consider hundreds of factors when gauging the relevance of a certain site or webpage. Search engines are constantly changing their proprietary algorithms – sometimes significantly – in an attempt to list only the most relevant results.
Major search engines vary their results by geographic region and language. For example, Google’s German page will place more emphasis on German websites. Search engines use various pieces of information; among these is language, the physical location of a website’s server, etc. Thus, the results from Google.de may differ from the results of Google.com.
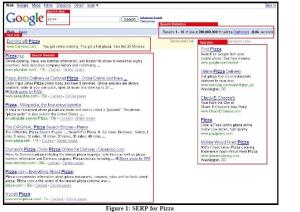
SEO is “keyword centric.” A major emphasis for professionals is to figure out what words or phrases a website’s target audience is likely to use when searching for a site’s content. Using this information, they strive to have the website appear within the first page of search results. SEO is strongly related to search engine marketing (SEM), which focuses on delivering advertisements that are relevant to an executed search. It is critical to the success of any SEO or website marketing campaign to have specific keywords in mind from the onset of the project. See Figure 1 to see where text ads appear on search results pages.
A website’s search engine “rank” refers to its position in the search engine’s results. There are factors that influence the rank of a website on SERPs that website administrators can control; others they cannot.
Controllable factors include page title tags, page content, the website’s architecture, and the ease at which a web “spider” can examine a site. A web spider is a website discovery program deployed by search engines that scans the Internet looking for new pages and content changes on pages it has already discovered. There is little control over what competing websites can do to increase their search engine ranking; these actions may result in the down-ranking of other sites. Furthermore, website administrators sometimes can influence which other websites will link to their own site and how they will do so.
Original Source: What is SEO , SEO_Basics